Success Story: Supercomputer Applications in Biomedical Engineering
NCC-BULGARIA

The National Competence Centre of Bulgaria (NCC-Bulgaria) in the area of High-Performance Computing (HPC), High-Performance Data Analytics (HPDA) and Artificial Intelligence (AI) has the goal to enhance and develop the competences of the Bulgarian computational community, making full use of EuroHPC resources and the EuroCC partnership.
The NCC-Bulgaria is built by a consortium coordinated by the Institute of Information and Communication Technologies at the Bulgarian Academy of Sciences (IICT-BAS), and two members, Sofia University “St. Kliment Ohridski” (SU), and University of National and World Economy (UNWE). The three partners carry diverse technical and scientific background in the area of HPC and ICT in general, so as to ensure achievement of the project objectives and guarantee the overall success.
The partners collaborate with Sofia Tech Park, where the Discoverer EuroHPC supercomputer is operating.
Industrial organisations Involved:

Established in 1995 AMET Ltd. is a company dedicated to development, modern manufacturing and distribution of electronic medical equipment and modules. It is a reliable and desired partner in both the Bulgarian and the foreign market. The partnership with IICT-BAS is directly based on the development of computer models and their efficient implementation on HPC systems. The results of the joint projects are new products or/and upgraded ones including smart electrosurgical instruments and physiotherapy equipment.
Technical/scientific Challenge:
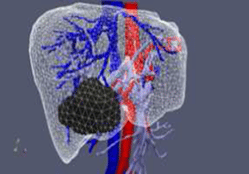
To develop a supercomputer model of the processes of Radio-Frequency (RF) Liver Ablation (a treatment based on RF alternating current flow, delivered by a needle-like probe, that destroys the undesired tumor tissue via heating). Up to O(109) unknowns with respect to space variables and O(104) time steps are needed to resolve the complex geometry.
To numerically analyse the temperature field within the impact region of a portable device for contact-free removing ticks. A computer model based on a system of Partial Differential Equations has been developed. The computational region possesses a complicated, multi-layer geometry, leading to strong mesh and coefficient anisotropy.
Business impact:
High-frequency electro surgery is one of the most commonly used in practice surgical technique. Today this method is present in every surgery in the world. One of the specific areas of impact of the developed HPC solutions is the radio-frequency tumor ablation. The aim of the joint work with AMET Ltd is to respond to the ever-increasing need for more precise intervention, both for intervention in hardly accessible places and for maximally low-invasive intervention.
The developed software tools for supercomputer simulation of coupled physical processes of radiofrequency electro surgery manipulations are beyond the scope of available commercial packages.
Measurable indicators are applied to assess the reliability of the obtained results, thus providing proven criteria for minimizing subjective inaccuracies. The impact of using large-scale HPC models reached more than two times improved precision of evaluating the volume of effectively ablated tissue.
The business impact for the industrial partner includes: (i) improving the technology characteristics of existing products (e.g. hepatic tumor ablation); (ii) development of new products (e.g. contactless removal of blood-sucking parasites). An increase in the market share of AMET Ltd in the field of the studied electrosurgical technologies has been achieved.
Solution:
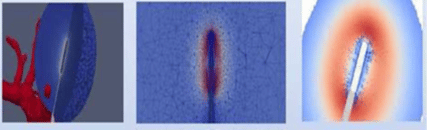
The processes are substantially three-dimensional and time-dependent (nonstationary).The parallel realization of the developed computer models involves integration of open-access parallel software packages, such as: Netgen, ParMETIS, Hypre, BoomerAMG, and ParaView. It is built upon a computational model with distributed memory, that allows for solving large-scale problems with O(109) DoFs. The realized computer models are strongly coupled. This determines the key role of the communications realized by MPI. It is shown that, due to the strongly inhomogeneous computational region, which gives rise to the necessity of a strongly unstructured triangulation, for the considered class of problems 1D and/or 2D domain decomposition (DD) leads to highly restricted parallelism. Thus, the application of ParMETIS for efficient 3D DD is vital.
Benefits:
- Fully realistic computer simulation of strongly coupled processes of RF electrosurgical technologies.
- Time/cost saving of parameter optimization of high tech low-invasive procedures.
- Assessment of complex processes hardly assessable for medical imaging.
SUCCESS STORY # HIGHLIGHTS:
- Keywords: Supercomputer applications; smart electrosurgical instruments; physiotherapy equipment; radio-frequency liver ablation; contact-free tick removal
- Industry sector: Biotechnology/Bioinformatics, Health care / Pharmaceuticals / Medical devices, Manufacturing & engineering
- Technology: HPC, AI for Big Data
Radio-frequency liver ablation simulations:
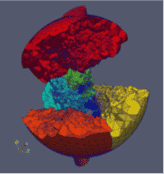
AMET Ltd. Portable device for removing ticks:

Contact:
Prof. Svetozar Margenov,
Assoc. Prof. Stanislav Harizanov,
Institute of Information and Communication Technologies,
Bulgarian Academy of Sciences
This project has received funding from the European High-Performance Computing Joint Undertaking (JU) under grant agreement No 951732. The JU receives support from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation program and Germany, Bulgaria, Austria, Croatia, Cyprus, the Czech Republic, Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Greece, Hungary, Ireland, Italy, Lithuania, Latvia, Poland, Portugal, Romania, Slovenia, Spain, Sweden, the United Kingdom, France, the Netherlands, Belgium, Luxembourg, Slovakia, Norway, Switzerland, Turkey, Republic of North Macedonia, Iceland, Montenegro