Success Story: Public Transport Analysis on HPC Infrastructure
NCC presenting the success story




TÜBİTAK-TRUBA, one of the two capacious HPC centers authoritatively in Turkey, coordinates NCC Turkey. The Middle East Technical University (METU), Sabanci University (SU), and Istanbul Technical University National Center for High-Performance Computing (UHeM) are third-party partners and cooperate with TÜBİTAK-TRUBA in the decision-making process. In a project, TÜBİTAK-TRUBA provides technical support to researchers and monitor running jobs. Furthermore, TÜBİTAK-TRUBA regularly organises online meetings with the researchers to discuss drawbacks and progressions. This project is conducted under the auspices of TÜBİTAK-TRUBA with the inspections mentioned above. On the researcher side, the METU researcher team performs the project and present the success story.
Technical/scientific Challenge:
Parabol has been developing a PT analysis platform (cermoni.app) to analyze the passengers’ boarding data and the vehicles’ GPS location data collected from a PT system. Currently, it performs spatiotemporal processing and analysis on the PT data, around 10M rows per month. Moreover, the PT accessibility analysis should be performed by finding activity regions for each commuter. Creating value from such big data to understand the mobility patterns involves 3D (space, time, and commuter) analysis which is time-consuming and is challenging. Hence, the spatiotemporal clustering algorithm for PT user activities (STCAPT) needs parallel execution.
Business impact:
Advanced algorithms have already been developed to provide more comprehensive analyses, such as Origin-Destination analysis to understand mobility patterns as a unique, high-tech decision support mechanism. The TRUBA HPC environment helps us reach this aim with highly improved performance. It is now possible to run these algorithms and take the results in a reasonable amount of time. Thus, such algorithms with parallel execution on HPC allow working with large-scale networks for NP-hard optimization issues. This creates a really fast, highly accurate, less costly, and more effective decision support mechanism not only for strategic or tactical but also for operational decisions. It gives our algorithms and hence the company a competitive advantage in the market.
Industrial Organisations Involved:

This success story results from a case study led by METU and TRUBA in collaboration with an SME, Parabol, located in METU’s Technopark. Parabol (paraboly.com) has been carrying out R&D activities in the intelligent transportation systems sector since 2011. By bringing together the company’s primary expertise areas (big data analytics, AI-based mobility algorithms, mobility analytics, mobility management, cloud computing) with R&D activities, they provide mobility management and analytics software instruments in 11 countries and +50 cities in three continents to improve different transportation modes such as public transport (PT) mobility.
Solution:
Considering the fact that STCAPT requires a large amount of memory to run, which an HPC environment can provide, we worked on developing an approach to run STCAPT on HPC. The algorithmic approach followed for parallelizing STCAPT contains first grouping the data by passenger id and then finding regions for each passenger.
We first developed an Apache Beam pipeline and deployed it on the Spark runner for its execution on HPC. However, since the execution of the Beam model failed, the pipeline was then ported to Apache Spark and executed successfully. Here, we developed two different Spark pipelines. The first one used Spark transforms and custom map operations on RDDs to generate passenger commute sequences. The next one used SparkSQL to aggregate those sequences to find an Origin-Destination matrix for some given grid. The output of the first pipeline is used as an input for the second one because showing outputs of the first on a map is not practical or useful. All these steps were guided by the METU team and supported by the TRUBA team, who installed and managed the Apache Spark platform on the HPC environment.
While the analysis cannot be completed reasonably on a typical server within the company data center, it took just minutes to run it with a test dataset on TRUBA. Being able to use an HPC infrastructure for this experiment gave us very impressive results. On a Spark cluster created with only three nodes of TRUBA, the test runs resulted in a 90% decrease in runtime.
Benefits:
- Ability to work in the HPC environment, especially to run Apache Spark pipelines.
- Understanding urban public transport mobility patterns much better.
- Saving time in getting results for complex optimization problems and operational decisions with highly-increased performance even for large-scale cities.
- Increasing the efficiency of public transport systems and accessing better public transport service levels.
SUCCESS STORY # HIGHLIGHTS:
- Keywords: Apache Spark, big data, HPDA, data analysis, smart city
- Industry Sector: Smart City, Intelligent Transportation Systems, Origin-Destination, Public Transportation
- Technology:Big Data, HPC, HPDA.
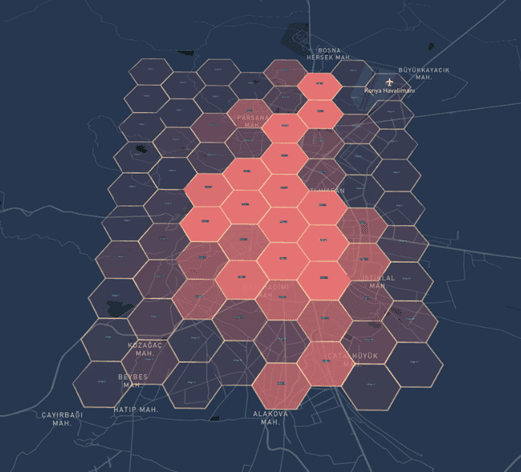
Figure 1: As a result of OD analysis, the origin density of PT trip during the morning peak.
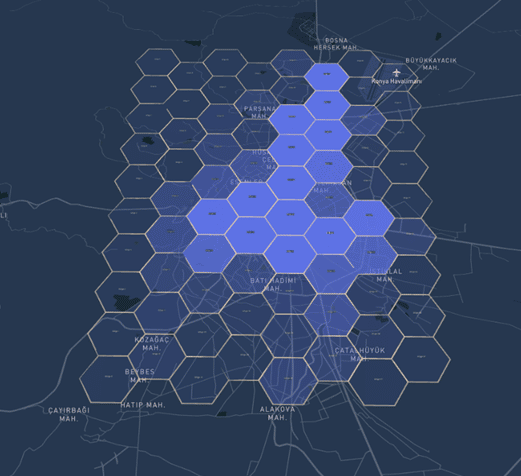
Figure 2: The destination density of PT trip in the morning peak (OD analysis)
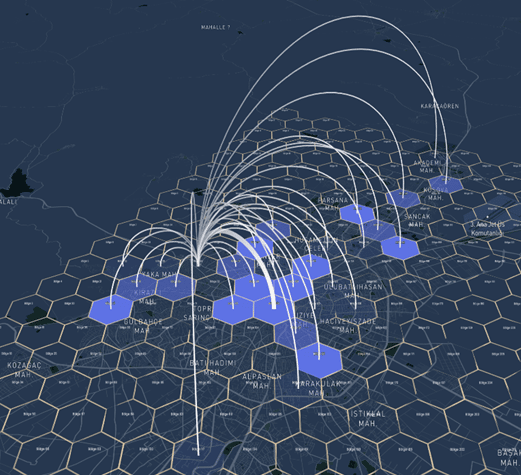
Figure 3: The density of destination zones of trips starting from the selected region.
Contact:
Metin BARIŞ, Parabol, metin.baris@paraboly.com
Cevat ŞENER, METU, sener@ceng.metu.edu.tr
This project has received funding from the European High-Performance Computing Joint Undertaking (JU) under grant agreement No 951732. The JU receives support from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation program and Germany, Bulgaria, Austria, Croatia, Cyprus, the Czech Republic, Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Greece, Hungary, Ireland, Italy, Lithuania, Latvia, Poland, Portugal, Romania, Slovenia, Spain, Sweden, the United Kingdom, France, the Netherlands, Belgium, Luxembourg, Slovakia, Norway, Switzerland, Turkey, Republic of North Macedonia, Iceland, Montenegro