Success Story: Environmental Data – From Transferring and Analytics to Decision Making
NCC-BULGARIA

NCC-Bulgaria is founded by the Institute of Information and Communication Technologies at the Bulgarian Academy of Sciences, the Sofia University “St. Kliment Ohridski” and the University of National and World Economy.
NCC-Bulgaria is focused on:
- Creating a roadmap for successful work in the field of high performance computing, big data analysis and artificial intelligence.
- Analyzing the existing competencies and facilitating the use of HPC/HPDA/AI in Bulgaria
- Raising awareness and promoting HPC/HPDA/AI use in companies and the public sector.
Industrial Organisations Involved:
Agricultural companies, using sensors for soil and meteorological factors monitoring
Companies working in the tourist sector – tour operators, event organizers
Technical/scientific Challenge:
Reliable, fast, and accurate transferring of environmental (meteorological) data, followed by its computational analysis (descriptive and predictive), is a considerable technical challenge. On one hand, it is difficult to methodologically organise the large volumes of data being transferred, the enormous diversity of environmental sensors used, and the proliferation of the transmission protocols. On the other hand, consistent assurance and maintenance of collected data quality while selecting the right tooling and algorithms for data analytics and presentation, requires specialised knowledge and technological experience.
Solution:
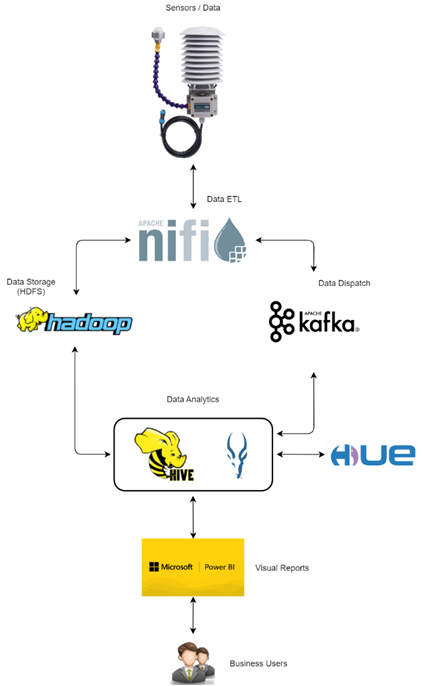
To solve those challenges, a referential IoT architecture is proposed, designed and implemented with the following components: data extraction and cleaning module NiFi, data distribution module Kafka, data storage module Hadoop HDFS, data analytics modules Hive, Impala and Hue, and data presentation module PowerBI. Building such an architecture enables flexibility and speed in data loading and clean up from a multitude of meteorological sensors, different networks and protocols, reliable ingestion, dispatch, consumption and storage of the extracted environmental physical values, powerful data analysis engines for both streaming and batch processing, for analysis and design of visual presentation of the results to be easily understood by all different types of users.
Business impact:
At the moment, there is a lack of real-time analytics and predictive instruments for forecasting bad weather conditions, alerting for emergency situations and natural disasters.
Real-time analytics of meteorological data could contribute to lowering risks, saving human lives and health, decreasing business losses, preventing unexpected and undesirable consequences.
The developed solution could support:
- Tourist companies, organizing tours and events
- Companies in the hotel industry sector – climate analysis for hotel chain expansion
- Companies in the agricultural sector – for business processes optimization (providing optimal conditions for growing crops), improving product quality, minimizing risks, etc.
Benefits:
- Flexible and reliable, multi-protocol and multi-network data extraction
- Cost effective Open-Source components
- Distributed high availability file system and event dispatching system
- Powerful data analytics including streaming and batch processing
- Sophisticated visualisation
SUCCESS STORY # HIGHLIGHTS:
- Keywords: IoT, Big Data, Environmental Data, Meteorology, Analytics, Apache Ecosystem, Reference Architecture
- Industry sector: Agriculture, Environment/climate/weather, IoT (Internet of things), IT/HPDA systems, services & software providers, Tourism
- Technology: IoT, Apache Ecosystem and HPC/HPDA Integration
Referential IoT Architecture for transferring and computational analysis of environmental (meteorological) data
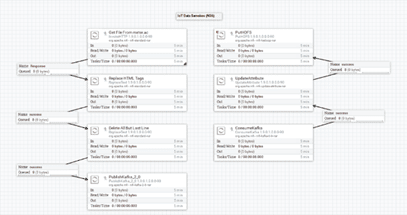
Environmental Data ETL
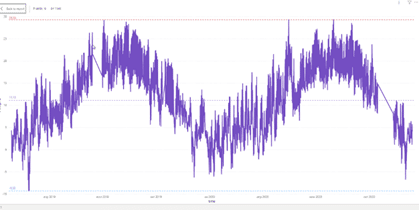
Environmental Data Report
Contact:
University of National and World Economy team (kstefanova@unwe.bg)
This project has received funding from the European High-Performance Computing Joint Undertaking (JU) under grant agreement No 951732. The JU receives support from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation program and Germany, Bulgaria, Austria, Croatia, Cyprus, the Czech Republic, Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Greece, Hungary, Ireland, Italy, Lithuania, Latvia, Poland, Portugal, Romania, Slovenia, Spain, Sweden, the United Kingdom, France, the Netherlands, Belgium, Luxembourg, Slovakia, Norway, Switzerland, Turkey, Republic of North Macedonia, Iceland, Montenegro